Black History Month,Asian American Month,Native American Month.Hispanic American..etc. I think that is because the real history is rarely taught. Sometimes it is taught without talking about the problems that people had in this country. Native Americans who survived the two new worlds coming together, suffered a lot that has never been taught. We don’t teach history and geography well. Many students never grasp the idea of the global exchange that is the world today.
Try this method. We have lots of ways to explore our histories today. We have technologies and books and real and virtual field trips.
USE THE DATE?
I had a teacher who used dates. She would say 1492? What was happening in the world?
We had to learn to create something that would tell her this information. Some students would have the dates before and after.You could not just memorize the data in a book or a chapter. It was a very interesting way to learn about what was going on in the world. ( Dr. Dannie Starre Townes- Virginia State University.
We had to learn what the leading influences were in the time frame that she gave us and then we had to present it to others.
I had a principal who had a book, the “Book of Where”, and she encouraged us to let students explore the travel of their families through the years.
The Book of Where: Or How to Be Naturally Geographic: Neill Bell
Published by Scholastic Inc, 1994
ISBN 10: 0590480154 / ISBN 13: 9780590480154

We made family maps and did International Day and learned about many cultures. Also the National Geographic had taught me to let kids draw a free hand map of the USA.
The family map was personal. It could be national or international. Cultural elements were inserted. Recipes were collected and shared.We shared family stories and history.
We explored geography and the US.
Now there are new ways to explore our history, our roots, our family stories.
Who are the people in your family ?
Where did the family originate?
Have you and your family always lived in the USA?
Where in the USA has your family lived, visited, what are the places that people have gone to school, and or work and or family vacations?
Is there another country that your family originated from? More than one?
Geography is a template for learning about the world.
Museums do tell the stories , the Smithsonian does workshops for interested people and there are exhibits. The Smithsonian had the exhibit years ago, Seeds of Change that used plants to tell the story of two worlds merging. Two old worlds merging and changing culture, or not from each other. The map above is a very simplified diagram. We have tools and technology now to tell the story better. There are new ways to explore museums. There are new ways to explore cultures. Google Cultural Institute
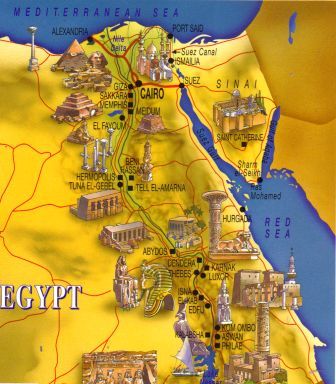
The Google Cultural Institute is a way to learn about cultures. You can explore using technology as in this virtual tour of Egypt.. (This is a view of the great Pyramids of Giza.)
There is this project that lets you learn from artifacts in a museum. It is the Smithsonian project X3D.
“The SIx3D viewer offers students the ability to explore some of the Smithsonian’s most treasured objects with a level of control that has never been possible until now. We hope this revolutionary level of access to the Smithsonian collections will spark your students’ curiosity and that the exploration of these objects will enable them to build lifelong observation and critical thinking skills.”
“With few exceptions, SIx3D also offers access to these data sets. Hailed by many as the third industrial revolution, 3D technology is molding a new K-12 STEM model. Students can use the same tools as professionals to become creators themselves. Whether students are printing invaluable museum objects or inventions of their own design, we hope the chance to bring objects to life will give students the opportunity to create imaginative and innovative work.”
To help you introduce 3D and its possibilities to your students, Smithsonian educators are working on new resources for K-12 classrooms.
Rather than glimpsing art & photography in the confines of rectangular frames, step into them in virtual reality with the Google Cardboard for supported smart phones. Here is the link to start those explorations.
Traditional Museum Resources? So many museums online.
This is one that lets us frame the thinking about the two old worlds that came together.
Seeds of Change: Five Plants That Transformed Mankind was a 1985 book by Henry Hobhouse which explains how the history of the world since Columbus linked America to Europe and has been changed by five plants.[1] It describes how mankind’s discovery, usage and trade of sugar, tea, cotton, the potato, and quinine have influenced history to make the modern world. The museum used that book as a beginning way to tell us the story ,it was fascinating!!
The focus seeds are: sugar, corn, the potato, disease, and the horse, selected says Viola “because of the human dimension to their story.” From the exhibition has also came another book called “Seeds of Change,” edited by Viola and and Carolyn Margolis, assistant director of the museum’s quincentenary programs. ( You may notice that tobacco , which was a seed of change was not addressed.
‘IMAGINE a world without pizza, Swiss chocolates, or French fries! Even harder, imagine Italy without the tomato or the {cowboy} without his horse,” says Herman J. Viola, the father of the massive new show “Seeds of Change” at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History.
The ideas merged and produced an expanded concept for the exhibition “Seeds of Change” that would focus on five seeds chosen from a list of nearly l00. As Viola says, this exhibition focuses on “an exchange of peoples, animals, plants, and diseases between Europe, Africa, and the Americas” over 500 years that began when the New and Old Worlds met.Mr. Viola, curator of the 400-object show, notes that before Columbus encountered the Americas none of those fixtures of modern life had been discovered.
Article excerpt
‘IMAGINE a world without pizza, Swiss chocolates, or French fries! Even harder, imagine Italy without the tomato or the {cowboy} without his horse,” says Herman J. Viola, the father of the massive new show “Seeds of Change” at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History.
Mr. Viola, curator of the 400-object show, notes that before Columbus encountered the Americas none of those fixtures of modern life had been discovered.
Learning history can be fun!!

What is History?
“History is for human self-knowledge. Knowing yourself means knowing, first, what it is to be a person; secondly, knowing what it is to be the kind of person you are; and thirdly, knowing what it is to be the person you are and nobody else is. Knowing yourself means knowing what you can do; and since nobody knows what they can do until they try, the only clue to what man can do is what man has done. The value of history, then, is that it teaches us what man has done and thus what man is.” R. G. Collingwood
Knowing other people’s stories helps us to understand sometimes their ways of seeing the world and their elements of culture. Simply we can cite, food , shelter, clothing, systems of education, and customs or traditions. But it can get much more complicated than that. See here . Elements of Culture. We made T-Shirts to define regions in the US. Other countries may also have regional differences, linked by the language, land and available food sources.
What is Geography and what does that have to do with History?
How Do We Learn it? Why Study Geography?
Sometimes, even effective, fun award-winning web and mobile study apps aren’t enough to sustain motivation to study Geography, if you don’t see its relevance to your life. It is not just about beautiful visuals and interesting places, The truth is that geography is a highly relevant and important type of knowledge for anyone to have.
Here are some top reasons why you should study more geography.
- Global Awareness /Where is that place?
Let’s be honest: we all care about what other people think of us. That’s why our first important reason for studying geography is that it makes you look smart. Knowing basic geography can help you avoid embarrassing moments, impress a people, increase your knowledge of the world that we live in. In addition you see and hear about lots of places that are dots on the map. What do you really , really know about the places and the people who live there?
2. Put the News in Context
How are you supposed to understand the news if you don’t know geography? Knowing geography helps put current events in context. Recently there has been a lot of news about immigrants. Who are they , why do they come, where do they come from and what do we need to know about them or immigration in an historical sense. I was amazed to be in a city in Europe from which many Italians came and to see their letters of credit on a rope that was put up into the ceiling each night. This was when Italians were coming to America in droves from Naples.
For example, knowing that Hong Kong is a city in southern China can begin to help a person understand why it is politically different from the rest of China: it’s geographically isolated.

3. Chart the Course of History
Geography not only puts current events in perspective, it help us understand history. A person can’t understand World War II without understanding the roles of the continental Russian Winter or the English Channel. Geography shapes the course of world history. Want to better understand history? Study geography.
The various months help us to know the history in the United States of the groups who were brought here, who were already here, and those who immigrated here. I learned oter people’s history too. Here is a reason that people immigrate.
4. Build Navigation Skills
The most basic skill in navigation is understanding the “lay of the land.” Studying geography helps develop spatial thinking. Those skills could come in handy if you get lost driving around town or in the wilderness!Whoa.. did I forget the GIS? ESRI skills? You can build a story of the places you are studying on a map.
5. Travel Smart Whether doing Virtual or Real Travel.
Without a basic sense of geography, it’s impossible to get the most out of travel experiences. If you’re heading to Spain, do you want to see misty mountains, rocky coastlines, or searing-hot cities? These questions will decide whether you head to Torla, Basque Country, or Sevilla. Study up before your next vacation or VR Experience..You don’t want to do eye candy where you just look at pretty pictures without the content.

6. Understand Your Home
Geography allows you to understand the place where you live in the context of the world as it is. Why did people settle in your town? What is the cultural heritage of your town ? Your region?The people who live there? I just found out that the city that I grew up in was the home of slavery. Alexandria , Virginia. People were sold from that city to the south. I never knew that!.It was not taught to me. I went to a Catholic School at first, run by Irish Priesrs and nuns from the Oblate Sisters of Providence. I knew the history of Ireland, and of New Orleans from where the nuns came.
People settle in specific places because of the landscape. For example, cities are almost always built on a river or other reliable water supply. What is the history of the place you live? How has the geography affected the area? These are the questions to ask to gain a deep understanding of your home.
7. Get a Grasp on Globalization
Globalization has been one of the biggest forces in world history for decades. The saying “it’s a small world” reflects this change: the world is as big as it always was, but it’s just more interconnected than ever. Understanding the changes that have swept the world as a result of this interconnection is impossible without appreciating the geography on which it is taking place.

8. Make Sense of Different Cultures
Human culture is fundamentally place-based: the land determines or influences the cuisine, clothing, architecture, even social relationships. Every aspect of a culture is affected by its geography.
Geography helps you understand and appreciate the incredible diversity of cultures around the world. Like with news, geography puts culture in context. To understand a people, you have to know something about their land.

9. Prepare for the Future
Geographic skills guide important decisions every day. From architecture to politics to business, the physical landscape frames the debates happening today that will be in the history books tomorrow.
Most people don’t get to learn geography. It may be shared in the context of a place name on the news, or as a part of personal history, if there is interest.
Do your personal exploration and share it with others.

















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-557205813-5941861b3df78c537b8da273.jpg)







 The topics were the beginning of real science study for many students.
The topics were the beginning of real science study for many students.










 I have traveled to Egypt by thought, by reading, by books, by lectures in geography and by invitation of a friend. My quest was to visit the museum of antiquties in Cairo. Before the newest of technology, I had a laser disc of a mummy, and how they prepared it and like many others , I had done a lot of reading about Sir Howard Carter and his discovery. I also followed an archaeologist on television to see them examine new sites and try to identify new mummies, or tombs. In school for students I had a remarkable book to use with various movies and videos , by David McCauley.
I have traveled to Egypt by thought, by reading, by books, by lectures in geography and by invitation of a friend. My quest was to visit the museum of antiquties in Cairo. Before the newest of technology, I had a laser disc of a mummy, and how they prepared it and like many others , I had done a lot of reading about Sir Howard Carter and his discovery. I also followed an archaeologist on television to see them examine new sites and try to identify new mummies, or tombs. In school for students I had a remarkable book to use with various movies and videos , by David McCauley.