Have you seen?
Have you seen?
The report on Unequal Schools from the Civil Rights Commission
“The federal government must take bold action to address inequitable funding in our nation’s public schools.”
So begins a list of recommendations released Thursday by the U.S. Commission on Civil Rights, an independent, bipartisan agency created by Congress in 1957 to investigate civil rights complaints. Thursday’s report comes after a lengthy investigation into how America’s schools are funded and why so many that serve poor and minority students aren’t getting the resources they say they need.
The 150-page report, titled “Public Education Funding Inequity: In An Era Of Increasing Concentration Of Poverty and Resegregation,” reads like a footnoted walking tour through the many ways America’s education system fails vulnerable students — beginning with neighborhood schools that remain deeply segregated and continuing into classrooms where too many students lack access to skilled teachers, rigorous courses and equitable school funding.
“This report excavates the enduring truism that American public schooling is, and has been, profoundly unequal in the opportunity delivered to students, the dollars spent to educate students, and the determinations of which students are educated together,” writes the commission’s chair, Catherine Lhamon.
History lesson
The first two-thirds of the commission’s report is essentially a history lesson on the decades-old fight over equitable school funding, so we’ll start there, too. The fight arguably began in 1954 with Brown v. Board of Education and the Supreme Court’s decision that “separate but equal” schools for black and white students were anything but equal.
In 1965, President Lyndon Johnson waded into the debate, arguing that the federal government should send money to school districts that serve low-income families. Congress agreed, creating Title I. In the 2014-15 school year, states received more than $14 billion in Title I money.
To this day, though, states are all over the map when it comes to how equitably they spend their own money in schools. The problem was baked into the system from the beginning, with local property taxes being an important driver of both school funding and of inequities in school funding.
“This is America,” writes Karen Narasaki, a member of the commission. “Every child deserves a quality education that does not depend on their ZIP code.”
To make that happen — many states now use state tax revenue to try to even out those local imbalances, some more effectively than others.
We are a ‘Nation of Opportunity, and the present time points us toward the future.
There are groups that hope to change the way we learn by mentoring, by sharing, by participatory involvement at national, regional and local levels. School boards are often the passport to change. The National Science Foundation funds innovation and research.
Communities within groups like ISTE and CoSN help to drive change.They publish guides like
No Fear Coding
Computational Thinking Across the K-5 Curriculum
he people most affected by the inequality may not be a member or these groups trying to help them.
CoSN the Consortium for School Networking has action for members and reports such as this as well. AccessibilityToolkit.
CoSn also publishes the Horizon Report on an annual basis.

NMC Horizon Report
2017 Higher Education Edition
The NMC Horizon Report > 2017 Higher Education Edition is a collaborative effort between the NMC and the EDUCAUSE Learning Initiative (ELI). This 14th edition describes annual findings from the NMC Horizon Project, an ongoing research project designed to identify and describe emerging technologies likely to have an impact on learning, teaching, and creative inquiry in education. Six key trends, six significant challenges, and six important developments in educational technology are placed directly in the context of their likely impact on the core missions of universities and colleges. The three key sections of this report constitute a reference and straightforward technology-planning guide for educators, higher education leaders, administrators, policymakers, and technologists. It is our hope that this research will help to inform the choices that institutions are making about technology to improve, support, or extend teaching, learning, and creative inquiry in higher education across the globe. All of the topics were selected by an expert panel that represented a range of backgrounds and perspectives. View the work that produced the report on the official project wiki.
CIRCL takes us into the future using Cyberlearning.
New technologies change what and how people learn. Informed by learning science, cyberlearning is the use of new technology to create effective new learning experiences that were never possible or practical before. The cyberlearning movement advances learning of important content by:
- Applying scientific insights about how people learn
- Leveraging emerging technologies
- Designing transformative learning activities
- Engaging teachers and other practitioners
- Measuring deeper learning outcomes
- Emphasizing continuous improvement
2018?Horizon Report Update 2018
I am a pioneer in technology and use these sites to keep up. What do you and your communities use?
What about ACCESS?
While the nation continues to make progress in broadband deployment, many Americans still lack access to advanced, high-quality voice, data, graphics and video offerings, especially in rural areas and on Tribal lands, according to the 2016 Broadband Progress Report adopted by the Federal Communications Commission.
Section 706 of the Telecommunications Act of 1996 requires the FCC to report annually on whether advanced telecommunications capability “is being deployed to all Americans in a reasonable and timely fashion,” and to take “immediate action” if it is not. Congress defined advanced telecommunications capability as “high-quality” capability that allow users to “originate and receive high-quality voice, data, graphics, and video” services.
In the Report, the Commission determines that advanced telecommunications requires access to both fixed and mobile broadband services because more Americans use mobile services and devices to access the Internet for activities like navigation, communicating with family and friends and on social media, and receiving timely news updates away from home. The Commission also retains the existing speed benchmark of 25 Mbps download/3 Mbps upload (25 Mbps/3 Mbps) for fixed services, but finds that the current record is insufficient to set an appropriate speed benchmark for mobile service.
While the Commission finds that it is reasonable to apply the same speed benchmarks to all fixed services, including fixed terrestrial and fixed satellite broadband service, the Commission continues to observe different technical capabilities and adoption patterns between fixed terrestrial and fixed satellite service. Because no fixed satellite broadband service meets the 25 Mbps/3Mbps speed threshold as of the reporting period, the Report does not address the question of whether fixed satellite broadband services meeting this speed threshold would be considered to provide advanced telecommunications capability.
Significant progress in broadband deployment has been made, due in part to the Commission’s action to support broadband such as through its Universal Service programs. However, the Commission finds that these advances are not enough to ensure that advanced telecommunications capability is being deployed to all Americans in a timely way.
Key findings include the following:
- 10 percent of all Americans (34 million people) lack access to 25 Mbps/3 Mbps service.
- 39 percent of rural Americans (23 million people) lack access to 25 Mbps/3 Mbps.
- By contrast, only 4 percent of urban Americans lack access to 25 Mbps/3 Mbps broadband.
- The availability of fixed terrestrial services in rural America continues to lag behind urban America at all speeds: 20 percent lack access even to service at 4 Mbps/1 Mbps, down only 1 percent from 2011, and 31 percent lack access to 10 Mbps/1 Mbps, down only 4 percent from 2011.
- 41 percent of Americans living on Tribal lands (1.6 million people) lack access to 25 Mbps/3 Mbps broadband
- 68 percent living in rural areas of Tribal lands (1.3 million people) lack access.
- 66 percent of Americans living in U.S. territories (2.6 million people) lack access to 25 Mbps/3 Mbps broadband.
- 98 percent of those living in rural territorial areas (1.1 million people) lack access.
- Americans living in rural and urban areas adopt broadband at similar rates where 25 Mbps/ 3 Mbps service is available, 28 percent in rural areas and 30 percent in urban areas.
- While an increasing number of schools have high-speed connections, approximately 41 percent of schools, representing 47 percent of the nation’s students, lack the connectivity to meet the Commission’s short-term goal of 100 Mbps per 1,000 students/staff.
This Report concludes that more work needs to be done by the private and public sectors to expand robust broadband to all Americans in a timely way. The FCC will continue working to accelerate broadband deployment and to remove barriers to infrastructure investment, in part by direct subsidies, and in part by identifying and helping to reduce potential obstacles to deployment, competition, and adop
What about the use of the Internet in Rural Areas?
President Donald J. Trump signed on Monday two orders aimed at improving internet speeds in some of the country’s hardest-to-connect areas, a move he described as “the first step to expand access to broadband internet in rural America.”
The first executive order aims to make it easier for internet service providers to locate broadband infrastructure on federal land and buildings in rural parts of the country. The order notes that one of the consequences of slow, expensive internet service is that it hinders schools’ ability to “enrich student learning with digital tools.”
I found these items after a long search. Many of these articles are lost to parents, communities and interested advocates. The news is full of other things. Maybe these groups have to advocate for education as the press does not usually share important information, like the Horizon Report, and ISTE Standards.

Parents and communities often have their own definition of what works in education and they may not be up to date on the reality of change within education. This report from the Civil Rights Commission probably is not seen by those without access to computers and technology.

An illustration picture shows a projection of binary code on a man holding a laptop computer, in an office in Warsaw June 24, 2013. REUTERS/Kacper Pempel
What do you know about Schools and the use of technology?What you know might be gated by the school or community in which you live and learn.
This is a briefing that should be shared by schools, parents, communities and school boards. Education-Inequity.pdf.
There are a lot of people who do not have a problem with screen time. They have little access to technology. A new group is looking to find a way to use CRA funding to help the communities most impacted by lack of connectivity.
There are a lot of people who have a screen or two, but who do not use the technology effectively.
Sometimes there are programs funded within a community by groups trying to erase the digital divide. HUD has a program that is supposed to help make the change. Connect Home. What might be a group within your community that is trying to solve the problem?
Connect Home is a public-private collaboration to narrow the digital divide for families with school-age children who live in HUD-assisted housing.
Connect Home creates a platform for community leaders, local governments, nonprofit organizations, and private industry to join together and produce locally-tailored solutions for narrowing the digital divide. Through these stakeholders’ specific commitments to provide free or low-cost broadband access, devices, and digital literacy training, Connect Home extends affordable access to low-income families, ensuring that high-speed Internet follows our children from their classrooms back to their homes.
How Connected is Your Community?
Here is a map to check your connectivity.
How are You Connected? ACCESS MAP
TECHNOLOGY HELPS US TO UNDERSTAND THE WORLD

STEM? There are free resources at Concord.org.
Groundbreaking and deeply digital learning
Concord is a nonprofit organization dedicated to creating innovative educational technology for STEM learning. They have pioneering work brings technology’s promise into reality for education worldwide.
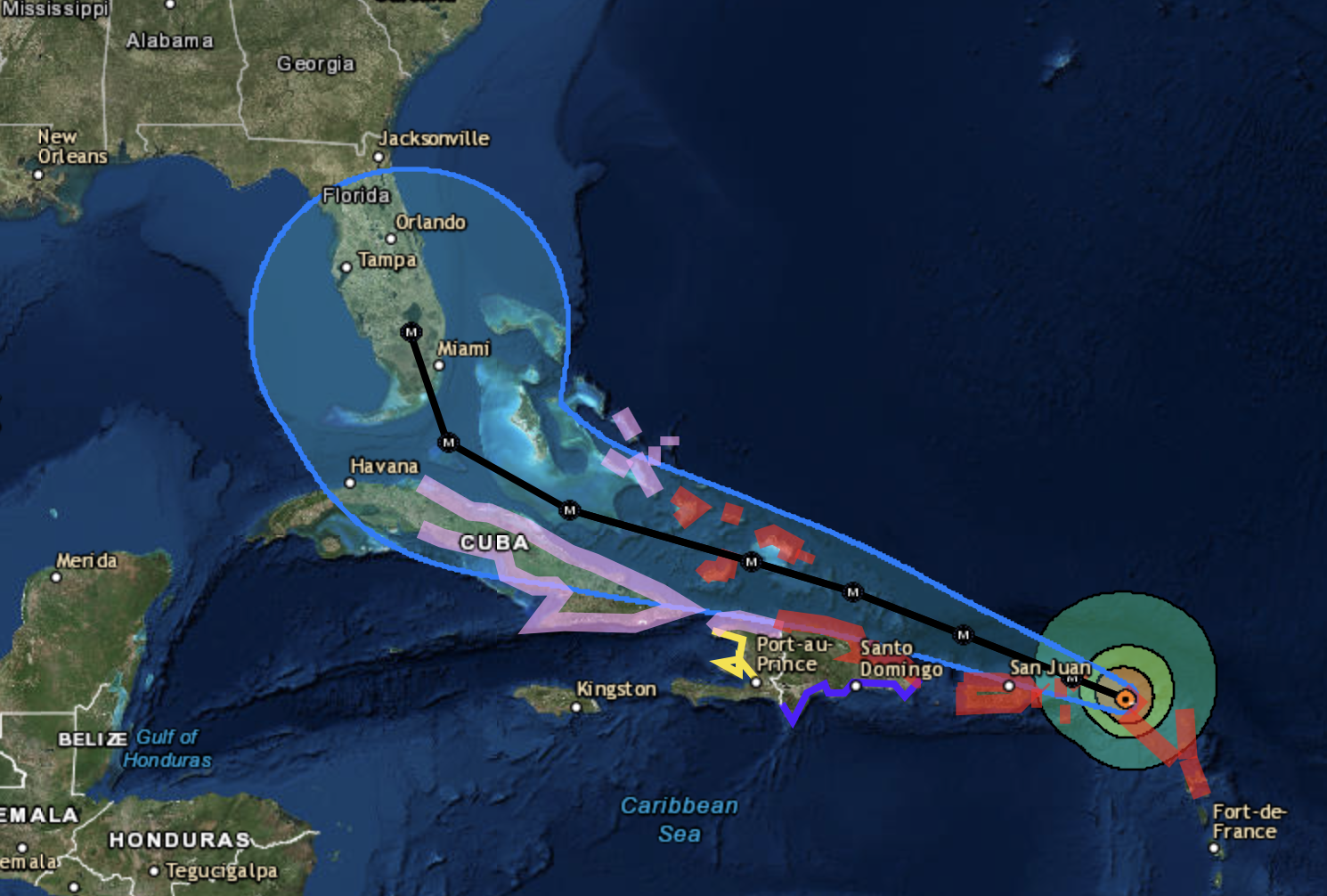
In recent months the use of technology has helped us to see disasters and to use big data to visualize.
This is an ESRI Story map of a weather event in the US.
Does your educational community take advantage of free resources, mentoring to schools and teachers in the ESRI Space?
Education ResourcesESRI Teacher Resources https://www.esri.com/en-us/industries/education/schools/educator-support















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-557205813-5941861b3df78c537b8da273.jpg)
 Have you seen?
Have you seen?









 The topics were the beginning of real science study for many students.
The topics were the beginning of real science study for many students.








 It is way past the year 2000. If you look around in your community, who is online and who is not? Who is meaningfully on line ? Who is coding, who is keyboarding while we in technology have moved on to new ways of working and new technologies.
It is way past the year 2000. If you look around in your community, who is online and who is not? Who is meaningfully on line ? Who is coding, who is keyboarding while we in technology have moved on to new ways of working and new technologies.
 The empowerment of the groups that are being left behind are addressed by leadership initiatives, such as that lead by Dr. Paul Resta and Dr. Robert McLaughlin.
The empowerment of the groups that are being left behind are addressed by leadership initiatives, such as that lead by Dr. Paul Resta and Dr. Robert McLaughlin. 







 . In a round table discussion with people who are in charge of learning places, museums and outreach at the Center for Cyberlearning Conference a remarkable thing happened . We broke down the silos and talked face to face about how to involve students in learning in places that are not school. Transportation and time are issues. Teachers do not often know the offerings of the local museums nor interact with the people who staff workshops and outreach.
. In a round table discussion with people who are in charge of learning places, museums and outreach at the Center for Cyberlearning Conference a remarkable thing happened . We broke down the silos and talked face to face about how to involve students in learning in places that are not school. Transportation and time are issues. Teachers do not often know the offerings of the local museums nor interact with the people who staff workshops and outreach.