
Recently a lot of articles and workshops have come to us about the digital divide and that it still exists. It is a relief that people are coming back to the realization that we have an uneven learning landscape. Here is a whole article. The following is an excerpt. This is a lot of information, but it is very important to understand the challenges in education.
“For children in the U.S., their homes, their communities, and their schools both represent and perpetuate inequity. In fact, the inequity of childhood is increasing, not shrinking.”
At the Broadband Summit hosted by the FCC and NTIA, I heard stories of people who are new to technology and how difficult it is for some populations to embrace technology. Many people are still waiting to embrace the mouse. Of course now we can leapfrog to a tablet. But understanding is the key to embracing technology in meaningful ways. Outstanding were the NTIA projects that support the uses of technology in community ways.
Sadly, many communities are still not well-connected.

SHARING THE VISION
In February, there was an uncommon event. It was the 2013 Broadband Summit ( Broadband Adoption and Usage- What Have We Learned?)NTIA and the FCC shared the day in sharing knowledge.
The FCC is a leader in encouraging the safe use of electronic media by children.Educators are held to the idea of digital textbooks while many do not have connectivity in their schools. Students do not have the skills for workforce readiness. Many teachers don/t have the skills they need to be effective in the use of technology. Some of these ideas are shared in Digital Nation from Edutopia.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=nKIu9yen5nc
From televisions to laptops to cell phones, electronic media have become some children’s almost constant companions. The commission provides parents with a variety of resources to improve children’s safety in today’s complex media landscape, including:
At the SITE Conference in New Orleans… we will share the results of our work and research so that you don’t have to guess about resources . We have a Facebook Grant. The work will be published in the society’s journals.Here is a little information to frame the research that has been conducted.What is SITE?
We are the Society for Information Technology & Teacher Education, and it is our mission to promote research, scholarship, collaboration, exchange and support.
SITE Conference 2013 – Teaching in Exponential Times!

The 24th Annual International SITE Conference will be held March 25 – 29, 2013 in New Orleans, LA, USA
DIGITAL CITIZENSHIP?
Definitions of Digital Citizenship In Our Facebook Grant Work
“Digital citizenship” is an umbrella term that covers a whole host of important issues. Broadly, it’s the guidelines for responsible, appropriate behavior when one is using technology. But specifically, it can cover anything from “netiquette” to cyber-bullying; technology access and the digital divide; online safety and privacy; copyright, plagiarism, and digital law, and more. In fact, some programs that teach digital citizenship have outlined no less than nine elements that intersect to inform a well-equipped digital citizen. It’s an overwhelming array of skills to be taught and topics to explore.The source of the nine elements is ISTE.org.
But while there is much talk about the importance of teaching digital citizenship in this information society, not many are sure what that really looks like. What tools are out there for teaching it? And how in the world can teachers make time in an already overcrowded curriculum?What about those who do not have broadband access? Or limited bandwidth?
Digital Passport?
WHO USES TECHNOLOGY?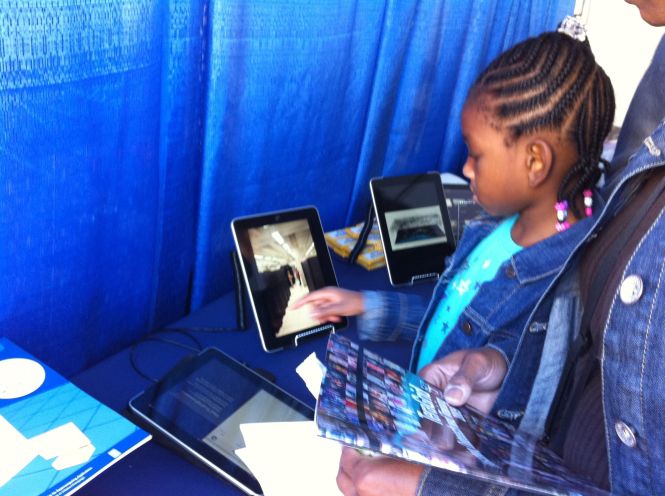
There are lots of users of technology. My concern is that there are people who do not use, know about or are interested in the use of technology , nor do they know how they benefit from the ways in which technology is used at the highest levels in Supercomputing. They innocently use GPS, weather resources from Supercomputing, watch on television the news from around the world, get climate updates, and earthquake and seismic information without thinking of the source. They get visualization and modeling examples daily, and do not think at all of computational thinking , problem solving and the math that is required to be able to participate in computing.Many people use the cloud without knowledge of what it is. A good reference or starting point is at Shodor.org.
There is a higher form of computing that facilitates a lot of tasks for us and few people seem to be aware of it.
You will hear people say, I don’t need technology. Sure. Invisible uses are everywhere.
It is called Supercomputing.
GOT BROADBAND?
This morning several articles caught my eye. But more than the articles is the interesting interaction on-line and the discussions about have and have-nots. Friends of mine, a professor, a code writer and a mathematician had a late night discussion following my posting this video by Jeannette Wing.
Dr. Jeannette Wing was the Assistant Director for Computer and Information Science and Engineering (CISE) Directorate at the National Science Foundation.Social Media helps us to communicate, though we may not always agree, at least there is the opportunity to exchange ideas and to think deeply with reflection. Dr. Wing has moved into the private sector. Microsoft announced that it has hired Dr. Jeannette Wing as Vice President of its Research division. Microsoft Research is an expansive group of technologists, scientists, and dreamers that build technology that may, or perhaps more often may not make it to market.
GOT PEDAGOGICAL KNOWLEDGE?
Such interesting conversations I have on Facebook. This is what I am talking about as a model for use of technology. It is not happening in most inner city and rural and distant schools. People have the tools but not the pedagogical knowledge of integration . ( TPACK)

The TPACK Model
The TPACK Model was created in response to the need to provide a framework around the important pieces of innovating learning with a focus on Technology, Pedagogy, and Content Knowledge. The overlap of these three components is where the 21st Century classroom is most powerful.
Here is general information on TPACK
Got Computational Thinking?
Computational thinking will be a fundamental skill used by everyone in the world. To reading, writing, and arithmetic, lets add computational thinking to every child’s analytical ability. Computational thinking is an approach to solving problems, building systems, and understanding human behavior that draws on the power and limits of computing. While computational thinking has already begun to influence many disciplines, from the sciences to the humanities, the best is yet to come.Looking to the future, we can anticipate even more profound impact of computational thinking on science, technology, and society: on the ways new discoveries will be made, innovation will occur, and cultures will evolve.
It is this that we learn with. So we had a person who writes code, a scientist and me, a teacher.. in a late night discussion with a professor about the video.This is one of the things about social media. It cuts the silos. Ground truths in social media.
 I
I
In this interview from the Education Technology & Change blog, Henry Neeman from the University of Oklahoma describes the increasing accessibility of HPC.
“You may not see the supercomputers, but every single day supercomputing is making our lives better. Everything from the cars we drive to the weather forecast on TV to the movies we watch to the detergent bottles in our laundry rooms are made, or made better, by supercomputing. Today, there are a number of ways for citizens to access supercomputing. Often, these are known as “science gateways,” and they provide a simple interface to a complicated back end. An example is nanoHUB, which K-12 and postsecondary students can use to do nanotechnology simulations. In fact, the nanoHUB website has curricula and teaching materials that any teacher can put to work in their classroom.”

early exposure and interest through outreach
This article caught my eye because it says the things that I have been blogging about, talking about and sharing for some time.
The article is entitled “By the Numbers: Teachers, Tech, and the Digital Divide” it extracts information from the latest Pew Report which is here. The new Pew Research survey of more than 2,400 middle school and high school teachers released today shows that, while teachers believe technology has helped with their teaching, it’s also brought new challenges — including the possibility of creating a bigger rift between low-income and high-income students.

Reading first.. . and there is free technology of excellence….Many of us know the challenges first hand . Many of us work at different levels of understanding of the difficulty. Often people dismiss what we who are on the ground , in the classrooms and in the places of need as if what we are saying is untrue. We have children who cannot read. Technology can help solve that problem. Early learning is important. Books and technology work too.
We know that people use the tools of technology, but that expense is a problem. We know that the cell phone has brought many people to a mobile use of technology and that “bring your own device” has become the salvation for some schools.Mobile use was shared in the Wireless Technology conference.
Wireless EdTech Beyond Being There – The Mobile Future of Learning ( in case you missed it)
There are a few other pieces of research that affect those of us of diversity in very important ways. We have always known that the digital divide is a problem based on access to broadband, hardware and access to teachers who may not have achieved the transformational skills to use technology in meaningful ways.
Some examples of ways in which people are trying to help are:
By Sean Cavanagh in Education Week
“Can online graphic novels help teenagers cope with difficult social situations?
Are 3-D technologies a tool for helping English-learners acquire language skills outside traditional educational settings? And what about the potential for mobile apps that let students manipulate on-screen images with their fingers to help them learn fractions?”
“A federal program, still in its infancy, is supporting research that seeks to answer those and other questions by wedding partners that often operate in isolation—educational technology and scientific research on learning—with the goal of transforming teaching and learning in schools.”
The federal government has been funding projects focused on technology and education for decades, and it has backed research on cognition in many forms. But the relatively new program, called Cyberlearning: Transforming Education , is the National Science Foundation ’s attempt to create a space within the agency devoted to supporting research on advanced learning technologies.
Some of the beginning steps of the program were shared in a conference .
NSF Funds Research to Identify What Works
Jeremy Rochelle of SRI
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fHmR0G_NmsE
The conference, which was hosted at the National Geographic, involved SRI , and NSF
you can find the portal here.They invite you to help write pages for the cyber-learning topic areas listed below. Their aim is to develop definitions that are strong enough to show the direction of the field but open enough to allow for innovation (see Defining Cyber-learning, below). If you have expertise in any of these areas and would like to be involved in editing these pages, please email cyberlearning-info@sri.com to request a wiki account.
Here are the topics:
The Technology Enhanced Learning (TEL) project is also defining key TEL topics
This is the
portal for this important work.( http://cyberlearning.sri.com/w/index.php/Cyberlearning:Community_portal)
There are many teachers, educators, administrators who are still learning to understand these topics and so even with help from various groups trying to make a difference, the leap of faith is a broad one. Edutopia has a program that starts to share why we must go digital.
There are still people who resist personal and educational use of technology for various reasons. Many teachers have the tools,but not the know how or support or the ideational scaffolding that is needed to be technology fluent. The Pew Report outlined many of the things that I would say, but also lets us know that it is not just
those of us who talk about the digital divide and social justice who are complaining about lack of broadband, access, tools and support for learning the technology.
Digital Generation: Educators
There is no cost for exploring good practices in education at the site.
0.000000
0.000000
 Here is what I wrote when I was wishing and hoping to get Google Glass. I wanted it.. dreamed about it.
Here is what I wrote when I was wishing and hoping to get Google Glass. I wanted it.. dreamed about it.
 Ideas are popping.
Ideas are popping.























 The Minority Media and Telecommunications Council has long worked – and sometimes been at odds – with the Federal Communications Commission in MMTC’s efforts to ensure equal opportunity and civil rights in the mass media and telecommunications industries. To address FCC issues, MMTC recently invited four former FCC chairmen to an “FCC Chairs’ Roundtable” panel at its 2013 Broadband and Social Justice Summit. During the panel, the former chairmen provided a deeper look into the federal agency and revealed their thoughts on a few communications industry regulatory matters.
The Minority Media and Telecommunications Council has long worked – and sometimes been at odds – with the Federal Communications Commission in MMTC’s efforts to ensure equal opportunity and civil rights in the mass media and telecommunications industries. To address FCC issues, MMTC recently invited four former FCC chairmen to an “FCC Chairs’ Roundtable” panel at its 2013 Broadband and Social Justice Summit. During the panel, the former chairmen provided a deeper look into the federal agency and revealed their thoughts on a few communications industry regulatory matters.







 Steve Hebert for The New York TimesA sign in Kansas City encouraged residents to pre-register for Google Fiber.
Steve Hebert for The New York TimesA sign in Kansas City encouraged residents to pre-register for Google Fiber.
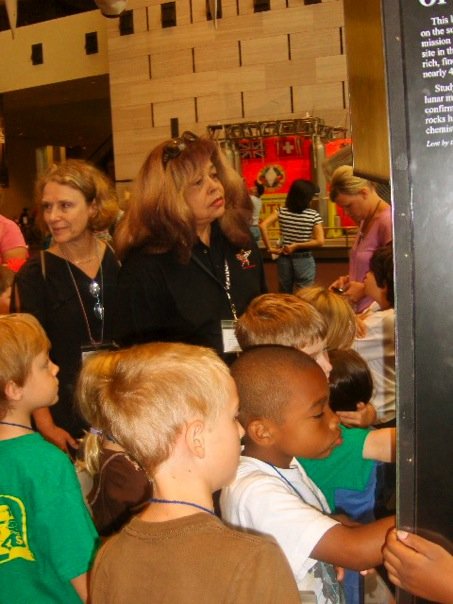








 Afterschool Universe training sessions are offered throughout the year at locations across the United States. Image Credit: NASA
Afterschool Universe training sessions are offered throughout the year at locations across the United States. Image Credit: NASA Hands-on activities play a role in each of the 12 Afterschool Universe sessions. Image Credit: NASA
Hands-on activities play a role in each of the 12 Afterschool Universe sessions. Image Credit: NASA